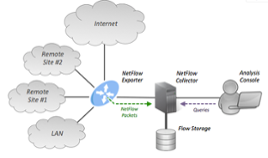
NetFlow is a feature that was introduced on Cisco routers that provides the ability to collect IP network traffic as it enters or exits an interface. By analyzing the data provided by NetFlow, a network administrator can determine things such as the source and destination of traffic, class of service, and the causes of congestion.
There are numerous key metrics when it comes to Netflow Monitoring:
1-Netflow Top Talkers
The flows that are generating the heaviest system traffic are known as the “top talkers.” The NetFlow Top Talkers feature allows flows to be sorted so that they can be viewed, to identify key users of the network.
2-Application Mapping
Application Mapping lets you configure the applications identified by NetFlow. You can add new applications, modify existing ones, or delete them. It’s also usually possible to associate an IP address with an application to help better track applications that are tied to specific servers.
3-Alert profiles
Alert profiles makes network monitoring using NetFlow easier. It allows for the Netflow system to be watching the traffic and alarming on threshold breaches or other traffic behaviors.
4-IP Grouping
You can create IP groups based on IP addresses and/or a combination of port and protocol. IP grouping is useful in tracking departmental bandwidth utilization, calculating bandwidth costs and ensuring appropriate usage of network bandwidth.
5-Netflow Based Security features
NetFlow provides IP flow information in the network. In the field of network security, IP flow information provided by NetFlow is used to analyze anomaly traffic. NetFlow based anomaly traffic analysis is an appropriate supplement to current signature-based NIDS.
6- Top Interfaces
Included in the Netflow Export information is the interface that the traffic passes through. This can be very useful when trying to diagnose network congestion, especially on lower bandwidth WAN interfaces as well as helping to plan capacity upgrades / downgrades for the future.
7- QoS traffic Monitoring
Most networks today enable some level of traffic prioritization. Multimedia traffic like VoIP and Video which are more susceptible to problems when there are network delays typically are tagged as higher priority than other traffic like web and email. Netflow can track which traffic is tagged with these priority levels. This enables network engineers to make sure that the traffic is being tagged appropriately.
8- AS Analysis
Most Netflow tools are able to also show the AS (Autonomous System) number and well known AS assignments for the IP traffic. This can be very useful in peer analysis as well as watching flows across the “border” of a network. For ISP’s and other large organizations this information can be helpful when performing traffic and network engineering analysis especially when the network is being redesigned or expanded.
9- Protocol analysis
One of the most basic metrics that Netflow can provide is a breakdown of TCP/IP protocols in use on the network like TCP, UDP, ICMP etc. This information is typically combined with port and IP address information to provide a complete view of the applications on the network.
10- Extensions with IPFIX
Although technically not NetFlow, IPFIX is fast becoming the preferred method of “flow-based” analysis. This is mainly due to the flexible structure of IPFIX which allows for variable length fields and proprietary vendor information. This is critical when trying to understand deeper level traffic metrics like HTTP host, URLs, messages and more.
Thanks to NMSaaS for the article.